The Navy's Iowa-Class Battleships are the Best Battleships Ever
Iowa, New Jersey, Missouri, and Wisconsin were decommissioned for the final time in 1990, 1991 1992, and 1991 respectively. All have since been converted to museum ship status; besides the Iowa museum already mentioned at the beginning of this article, New Jersey is berthed in Camden, NJ (appropriately enough), Missouri at Pearl Harbor, and Wisconsin in Norfolk, VA.
Summary and Key Points: The Iowa-class battleships, launched during WWII, are iconic symbols of U.S. naval power. Four ships—USS Iowa, USS New Jersey, USS Missouri, and USS Wisconsin—served in major conflicts from WWII to the Gulf War.
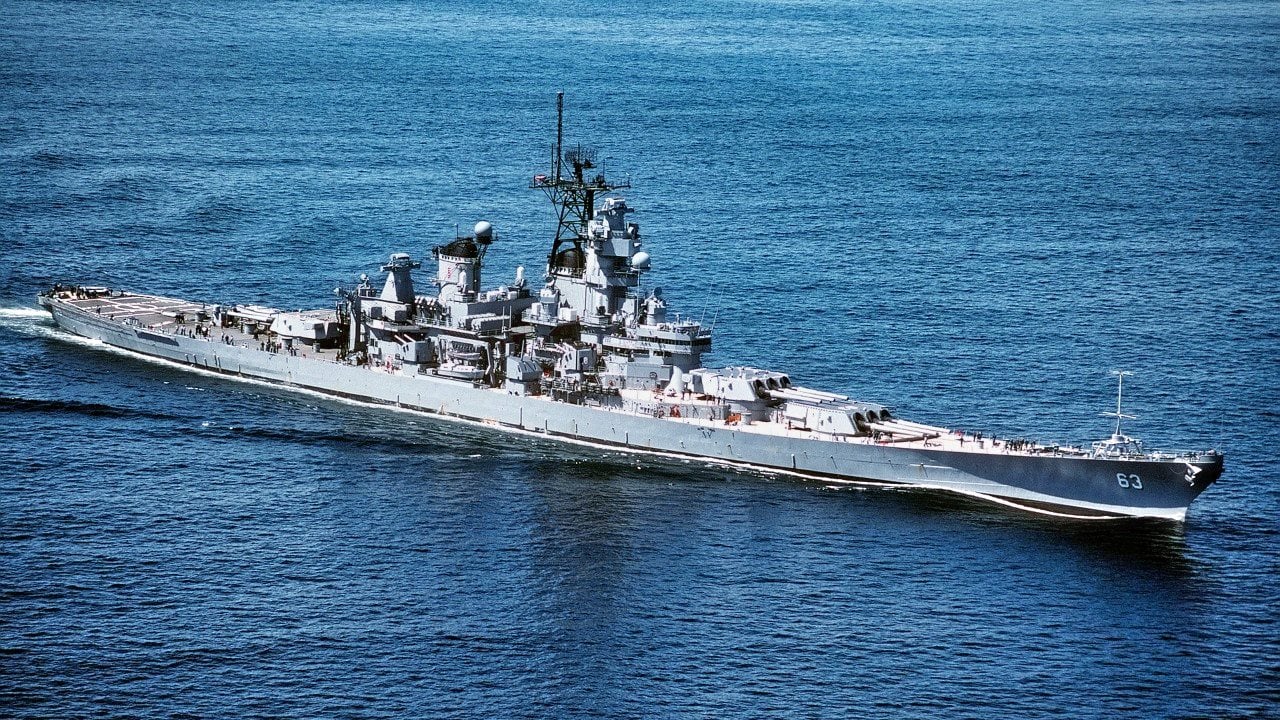

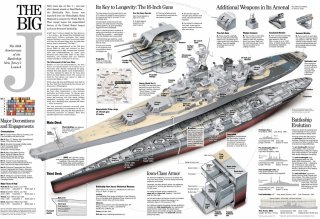
-Armed with nine 16-inch guns and renowned for their speed and firepower, these battleships were critical in various naval operations.
-The USS Missouri famously hosted Japan's surrender in 1945.
-All four ships are now museum exhibits, with USS Iowa located in Los Angeles Harbor, offering a glimpse into their storied past.
Exploring the Storied History of the Iowa-Class Battleships
Here's a fact you will appreciate: I've actually toured the USS Iowa (BB-61) on multiple occasions.
The Battleship USS Iowa Museum in Los Angeles Harbor/San Pedro has been open to the public since 2012, and it is a tour I highly recommend.
My personal friend Andrew Silber, now-retired former proprietor of the delightful Whale & Ale British Pub and Restaurant in San Pedro—a superb choice of venue for vittles and refreshments after you finish your ship tour—was one of the key local community leaders responsible for helping to bring the Iowa Museum to the Harbor.
Having said all that, let’s look at the history of this iconic battleship class:
The Berth, er, Birth, of the Battleships
The Iowa-class battleships trace their origins back to 1939 and 1940, i.e. before the bombing of Pearl Harbor crippled the U.S. Navy’s older pre-existing battleship fleet. Designed to meet the “escalator clause” of the Second London Naval Treaty via their 16-inch main guns and 45,000-long-ton standard displacement – though they actually ended up slightly overweight at 47,825 long tons – they were intended to intercept fast capital ships such as the Imperial Japanese Navy’s (IJN) Kongō class whilst also being capable of serving in a traditional battle line alongside slower battleships and act as its "fast wing.” A total of four such vessels were built: Iowa, New Jersey, Missouri (“The Mighty Mo”), and Wisconsin.
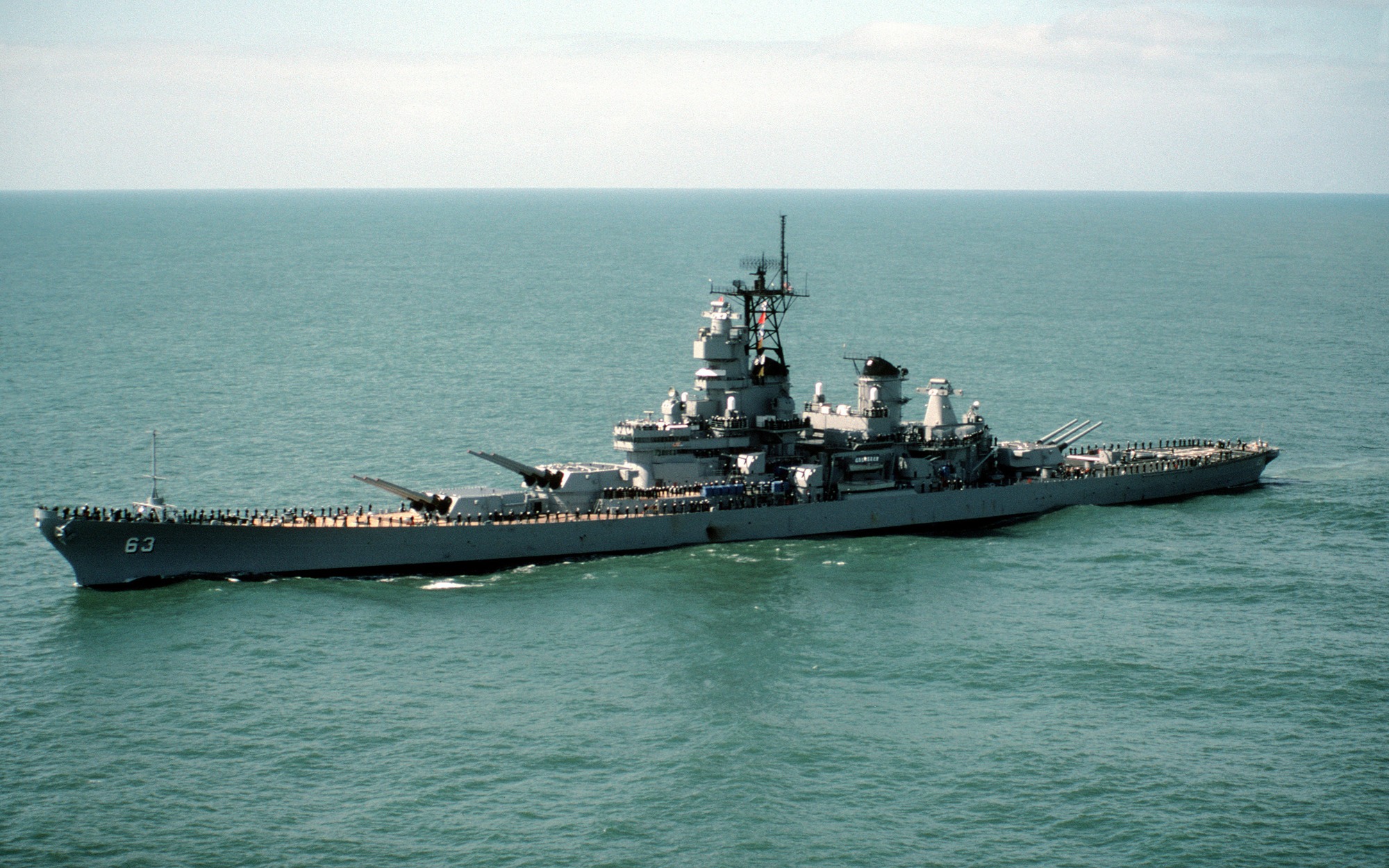

These big beasts carried nine of those aforementioned 16-inch guns – divvied amongst two turrets, fore and one aft – which could lob a 2,700-pound (1,225 kg) shell over a distance of 23.4 nautical miles (43.3 km). They are 860 feet (262.13 m) long at the waterline and 887 feet 3 inches (270.43 m) long overall with a beam of 108 feet 2 inches (32.97 m), and a Class A armor belt 12.1 inches (307 mm) thick.
Iowa-Class - As a Quick Aside
Interestingly enough, the Iowas never got to test their mettle against Japanese battleships or battlecruisers. The reason: only two WWII battleship-to-battleship engagements pitting the USN against the IJN involved other battleship classes: (1) the USS Washington BB-56), a North Carolina-class battleship which sank the Kirishima during the Second Naval Battle of Guadalcanal on 15 November 1942; and (2) the Surigao Stait phase of the Battle of Leyte Gulf, when Rear Admiral Jesse Oldendorf “crossed the T” of Vice Admiral Shōji Nishimura’s fleet, resulting in the sinking of the latter admiral’s battleships Fusō and Yamashiro – though the Fusō was sunk by destroyer torpedoes before the American BBs could get in their licks.
It was also an act of sweet revenge for Pearl Harbor, as out of the six U.S. battleships that participated—West Virginia, Maryland, Mississippi, Tennessee, California, and Pennsylvania—all except Mississippi had been sunk or damaged at Pearl and subsequently repaired or rebuilt, which goes to prove the old saying the payback is a … battleship (yeah, that’s it).
To this day, many seapower buffs love to hypothesize who would win in a “what-if” battle between the Iowas and the IJN’s biggest gun (as in 18-inchers) Yamato and Musashi.
A Piece of the Action…and Hosting a Sweet Surrender
Nonetheless, the Iowa-class behemoths still saw more than their fair share of combat action, from the Pacific Theater of WWII to Korea to Vietnam to Lebanon to Iraq. The overwhelming majority of these involved provided naval gunfire support (NGFS) against enemy shore batteries and installations (including on the main Japanese home island of Honshū), although the USS Iowa herself did have the satisfaction of engaging in at least one surface ship-to-ship battle, sinking the light cruiser Katori – with a loss of all hands, 315 officers and enlisted sailors – off of the island of Truk on 17 February 1944.
Arguably the biggest claim to fame for any Iowa-class warship was the Missouri’s hosting of the signing of the Japanese Instrument of Surrender on 02 September 1945, thus enabling the Iowa class to get the proverbial last laugh against Hideki Tojo.
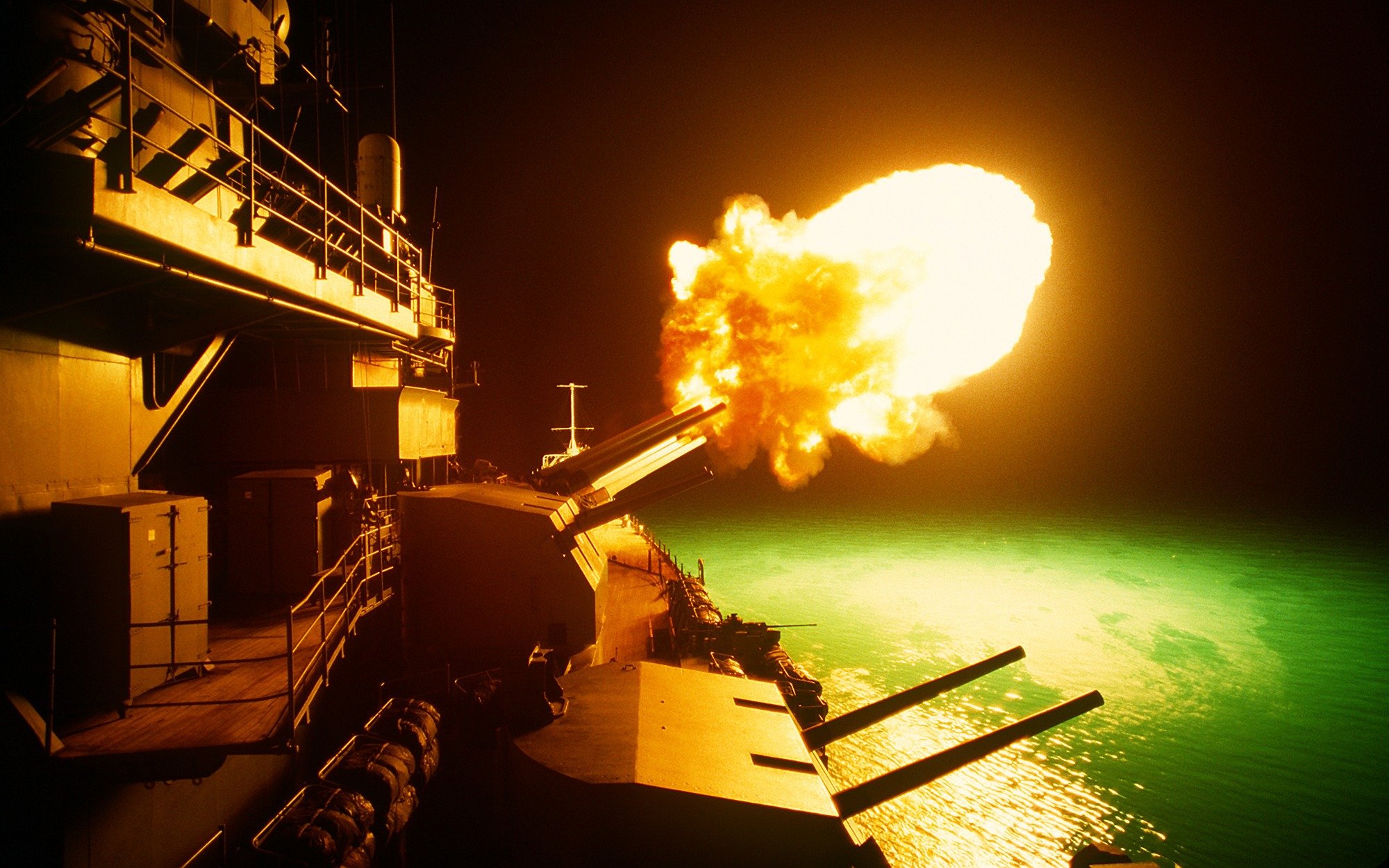
The Iowas’ last hurrah—indeed the last combat action for any battleship class—occurred during Operation Desert Storm in 1991, when the Wisconsin and Missouri combined to fire 1,078 16-inch shells at Iraqi targets. A somewhat amusing additional accomplishment during this same conflict occurred when some of Saddam Hussein’s troops surrendered to the Mighty Mo’s Pioneer UAV during the initial shelling on 24 February 1991, as it spotted targets for the mighty battlewagons—history’s first recorded surrender to a drone on a battlefield.

Iowa-Class - Where Are They Now?
Iowa, New Jersey, Missouri, and Wisconsin were decommissioned for the final time in 1990, 1991 1992, and 1991 respectively. All have since been converted to museum ship status; besides the Iowa museum already mentioned at the beginning of this article, New Jersey is berthed in Camden, NJ (appropriately enough), Missouri at Pearl Harbor, and Wisconsin in Norfolk, VA. The latter three are definitely bucket list items of mine.
About the Author
Christian D. Orr is a former Air Force officer, Federal law enforcement officer, and private military contractor (with assignments worked in Iraq, the United Arab Emirates, Kosovo, Japan, Germany, and the Pentagon). He has also been published in The Daily Torch and The Journal of Intelligence and Cyber Security.
Image Credit: Creative Commons.